No Code Indexing
Intro
Most novel products on Aptos require custom indexing. Unfortunately, custom indexing is hard for two key reasons:
- Devs must write code to describe their indexing logic.
- Devs must manage infrastructure to run an indexer.
The Geomi No Code Indexing platform solves both of these problems by eliminating the need to write code or run infrastructure yourself.
Learn how to use No Code Indexing in 116 seconds with this video:
Demonstration
Learn how to use Geomi No Code Indexing with this end-to-end demo, using the Petra Web Hong Bao experience as an example:
Resources referred to in the demo:
- Petra Web Hong Bao
- Hong Bao Move code
- Getting started with Hasura v2
- GraphQL Typescript codegen package
- GraphQL codegen example
Behavior
Merging events
To write multiple events into the same row a primary key must be specified. We merge on the specified PK:
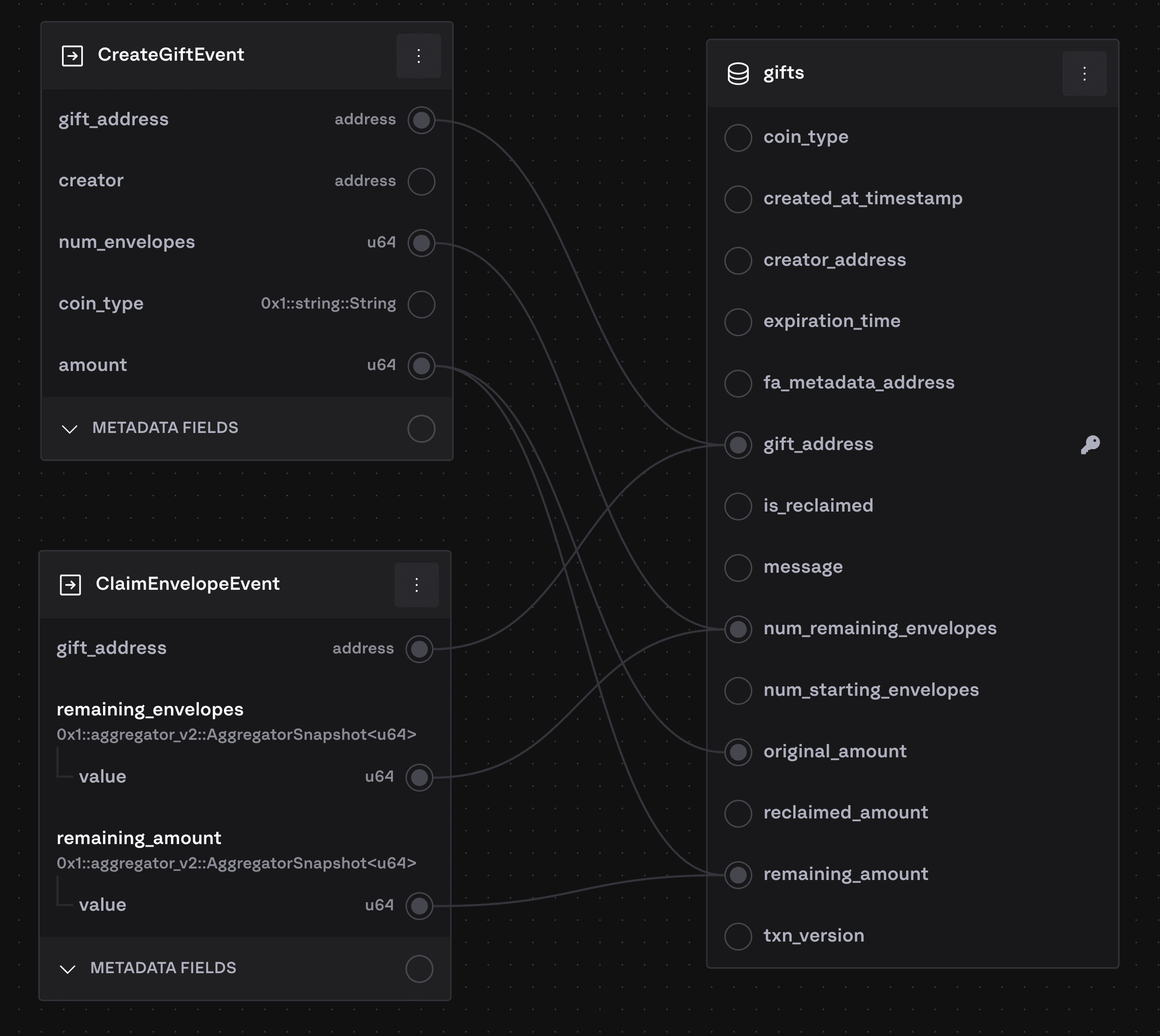
In this example, we upsert based on the gift_address field in the events. The flow will be something like this:
CreateGiftEventis indexed. There is no row in thegiftstable for this particulargift_addressyet, so we create a new row. For example, the value forremaining_amountis set based onamount.ClaimEnvelopeEventis indexed. There is already a row in thegiftstable for thisgift_address, so we update the existing row based on the values in that event rather than creating a new row. For example,remaining_amountin the row is updated based on$remaining_amount.valuein the event.
It is possible to configure a composite primary key (multiple fields comprise the primary key).
Upgrades
There are 4 types of upgrades. When you edit a processor, we will determine which kind of upgrade is required based on the edits you made to the processor config. You can choose to ignore this and choose a different upgrade type, but be careful, you might break your processor.
Hard Upgrade
When you make a breaking change to the config, such as changing the type of a field, we will do a hard upgrade. We also consider a hard upgrade required if you change the starting version.
Essentially “hard upgrading” is just creating an entirely new processor with the new config. We do not modify or delete the old processor as part of this upgrade process. This upgrade type is recommended for production dapps that are already live so you can gracefully migrate.
Once you have fully upgraded your dapp to use the new processor, you should delete the old processor.
In-place Upgrade (without backfill)
Certain config changes can be made without requiring a backfill. For example, if you remove a column from a table, we just delete that column and we’re done. Additive changes on the other hand, such as adding a new column or defining a new mapping, require a backfill to populated existing rows.
All we do in this place is update the config for the processor and restart it.
Warning: After this change, your Hasura metadata (their word for a config) might refer to a DB field that no longer exists, and therefore your metadata will be considered “inconsistent”. You can fix these issues in the console.
In-place Upgrade (with backfill)
This is the same as the above, but we will also run a backfill to populate any new fields. This is required for changes like adding a new column to a table or defining a new mapping. This option is also recommended if you need to update the processor’s starting version to an earlier point and backfill data from there.
Reset
Stop the processor, wipe the database, and restart with the new configuration. This operates in-place, it does not create a new processor. This is only recommended for processors still in active development as there will be downtime while the infra restarts and reindexes data.
Public API Access
When you enable public API access for your processor, anyone can query your processor’s API using their own API key. It has the following properties:
- Billing: The caller gets billed for API usage, not you.
- Access: Anyone with any valid API key can query this endpoint. The key does not have to be for a processor, a regular API key works too.
- Read-only: This endpoint is read-only, callers cannot write data or change your Hasura metadata.
The public URL follows the pattern:
https://api.{network}.aptoslabs.com/nocode/v1/public/{instance_id}/v1/graphqlTo enable or disable public API access:
- Navigate to the page for your processor.
- Click the three dots menu in the top right.
- Select “Enable Public API” or “Disable Public API”.
Considerations
Complex Types
- We support
Vec<T>. At the momentTmust be a primitive type (u8 → u256, address, String). It will becomeARRAYin the DB. - We support fields with generics, but don’t support indexing events that themselves have a generic type:
// This is supported.
#[event]
struct MyEvent has drop, store {
field1: MyStruct<u64>,
}
struct MyStruct<T> has drop,store {
my_value: T,
other_value: u16,
}
// This is not supported.
#[event]
struct MyEvent<T> has drop, store {
field1: T
}